Introduction
Group policies are an essential feature for administrators managing large networks, providing the ability to configure and enforce settings across multiple computers and users. This article explores how to navigate the Group Policy Object Editor, configure policy settings, manage administrative templates, and apply these settings effectively to streamline BigMIND deployment within an Active Directory environment. Understanding these concepts can significantly simplify the management of backup solutions and ensure consistent policy application across your organization.
Group Policy Overview
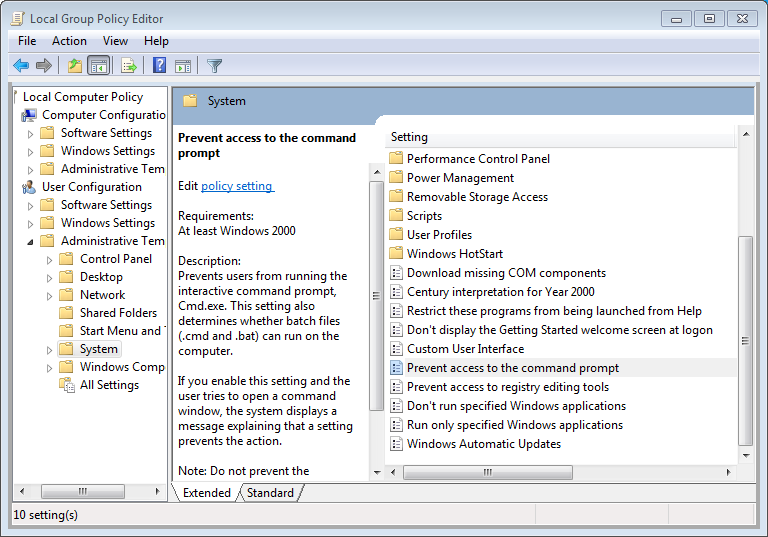
- In the Group Policy Object Editor, administrators encounter numerous policies that can be adjusted to control various aspects of user and computer behavior. For example, policies can regulate user access to certain functionalities, such as the command prompt.
- Group policies interact with the system registry, allowing modifications to any registry key associated with user and computer settings. Custom ADM files can be created to define these changes.
Editing Policy Settings
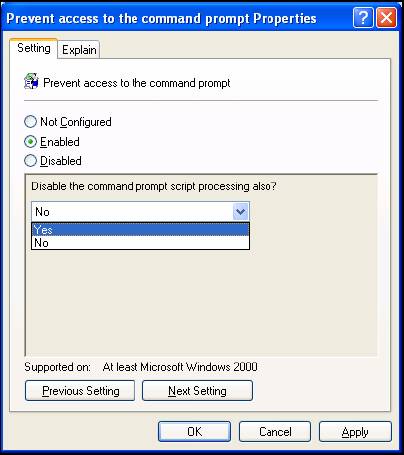
- To modify most policy settings, double-click the policy title within the Group Policy Object Editor. This action opens a dialog box with specific options relevant to the policy. The dialog box typically contains defining information about the selected policy setting.
Policy Settings Values
- Not Configured: Indicates no change is applied to the registry for this setting.
- Enabled: Updates the registry to reflect the GPO policy settings.
- Disabled: Removes the specific GPO policy settings from the registry.
Group Policy Sections
The Group Policy Object Editor comprises two primary sections:
- Computer Configuration: Contains settings applied to computers, effective at startup and during periodic background refreshes.
- User Configuration: Contains settings applied to users, effective at login and during periodic background refreshes. This section is further divided into categories such as Software Settings, Windows Settings, and Administrative Templates.
Managing Group Policies
The Group Policy Object Editor administrative tool is installed with Windows 2003-2012 Active Directory and can be accessed via:
- Group Policy Management Console (GPMC): A free Microsoft download recommended for managing Group Policies across multiple domains and sites. It offers a user-friendly interface with drag-and-drop functionality and supports backup, restore, import, copy, and reporting of GPOs.
- Active Directory Management Tools: Alternative access point for the Group Policy Object Editor.
ADM Files
Administrative Template files (ADM) are used to populate user interface settings in the Group Policy Object Editor, allowing for the management of registry-based policy settings. ADM files are available from Microsoft for OS and application policy settings and can also be created by administrators.
Adding Administrative Template files
To add ADM files in the GPO editor:
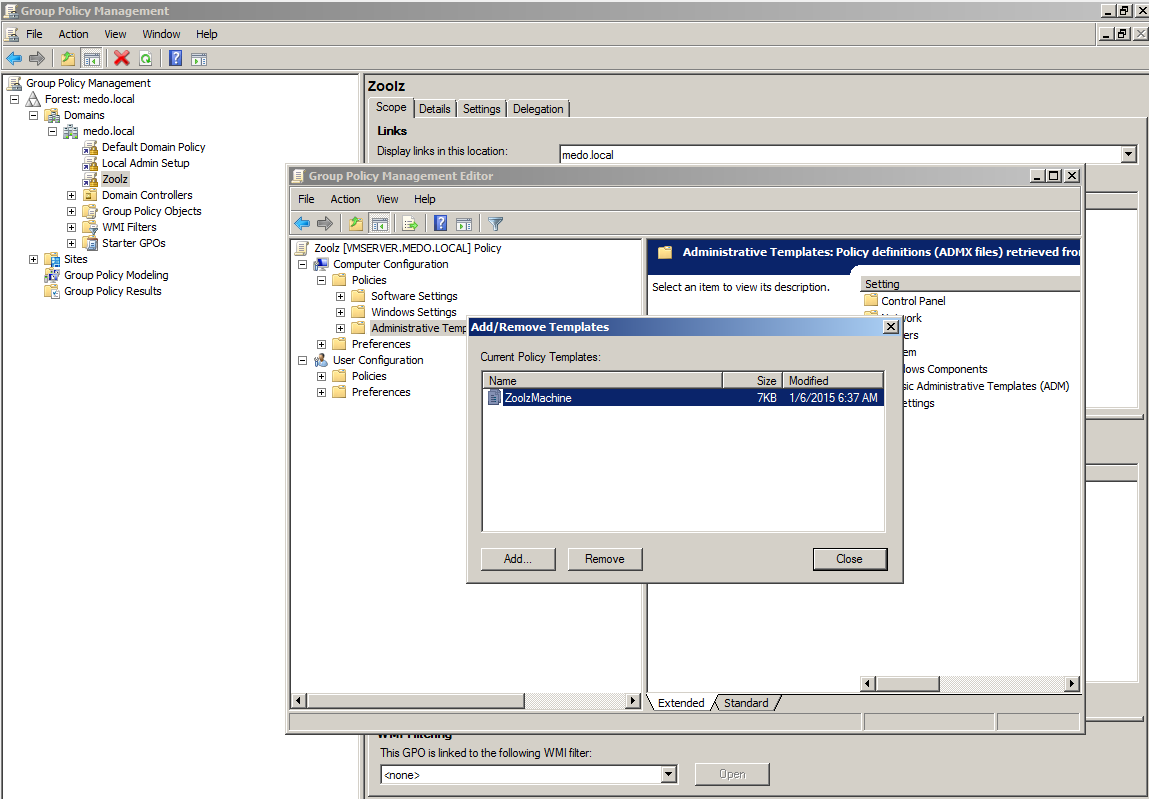
- In the GPO editor, right-click on Administrative Templates and Select Add/Remove Templates.
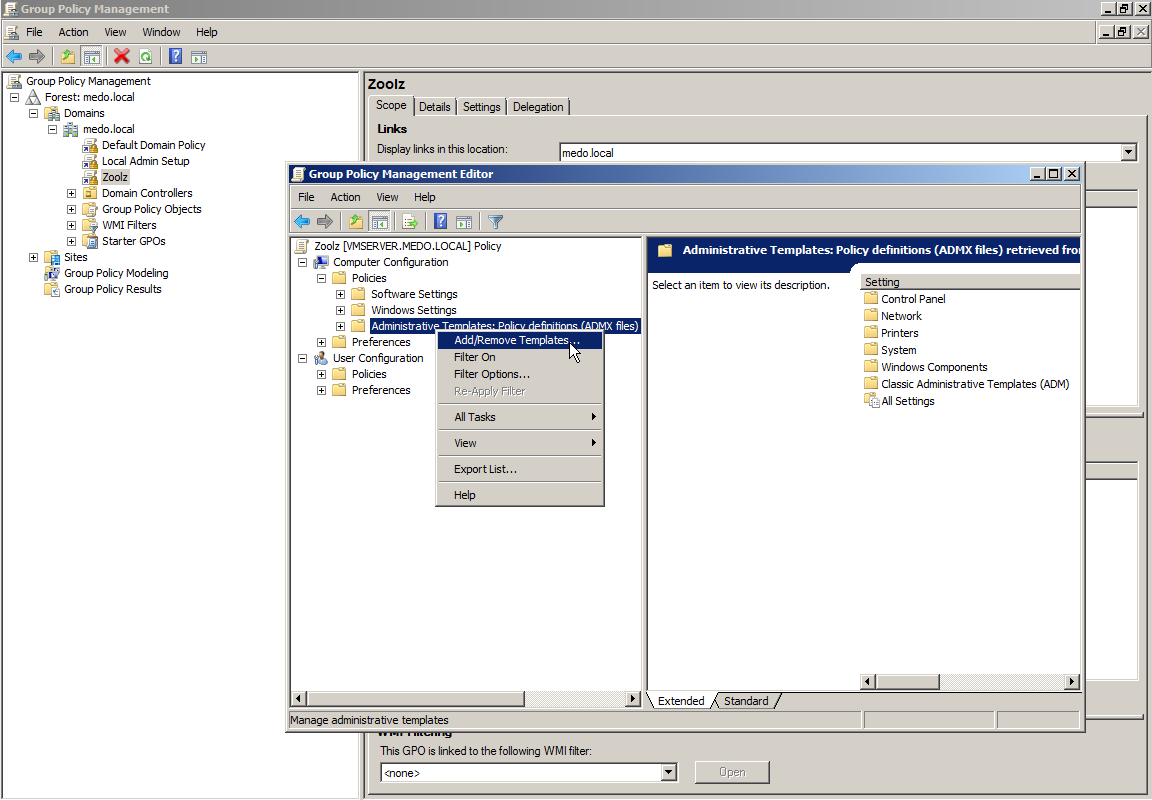
- Select Add to add a template.
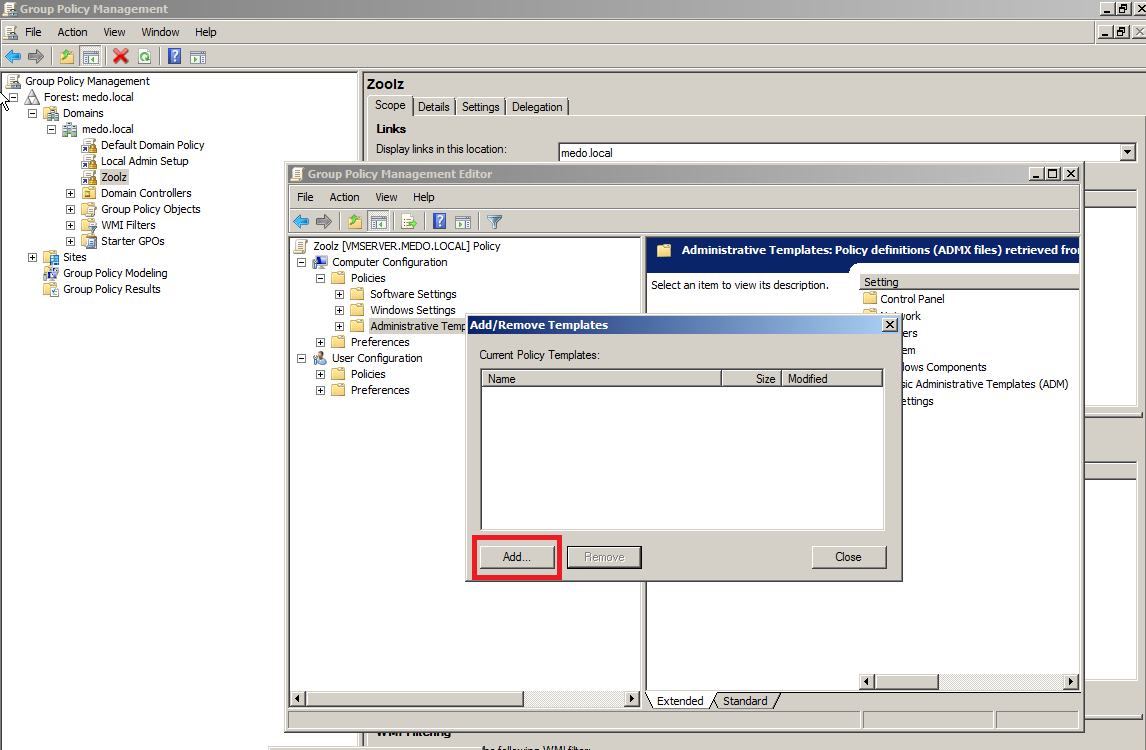
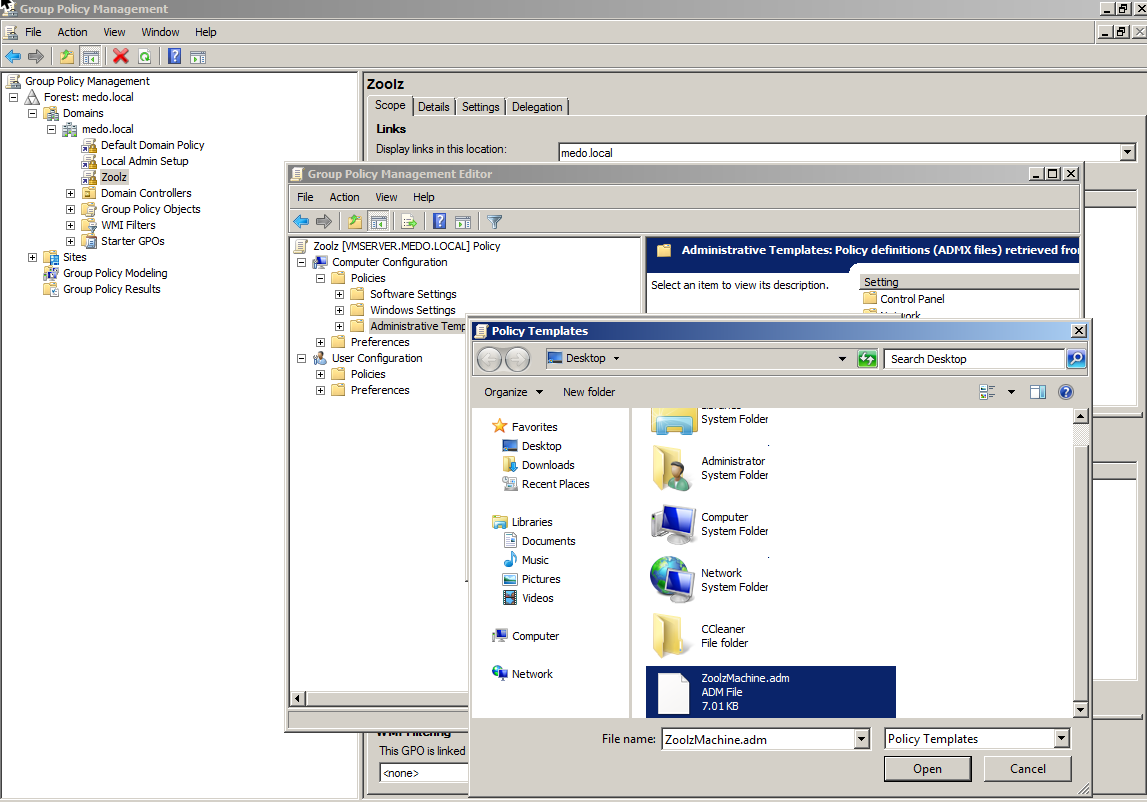
- Browse through the directory that contains the ADM file and select OK.
Group Policy Refresh Interval
- Group policies do not refresh immediately upon changes.
- By default, Windows XP, Vista, 7, and 8 update every 90 minutes in a domain environment.
- Local Group Policy changes occur within 0-5 minutes.
- To manually refresh Group Policy settings, use the command:
gpupdate /force
GPO Backup Settings
When deploying BigMIND through Active Directory, understanding how to use ADM files for effective deployment is crucial. For more details, refer to this article.
BigMIND Group Policy Settings and the Registry
Enabled policies are stored in the registry under: HKLM or HKCU\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\CloudBackup, followed by the specific product and GPO item.
Exporting CloudBackup Group Policy Settings from the Registry
- Right-click the product branch in the registry and select Export.
- Type the registration file name you want to save it as and click Save.
Importing Settings from a Registry File
For machines outside the domain, you can manually import registry settings by:
- Double-clicking the .reg file.
- Using the command line:
reg import filename.reg
- Or for silent imports:
regedit /s filename.reg